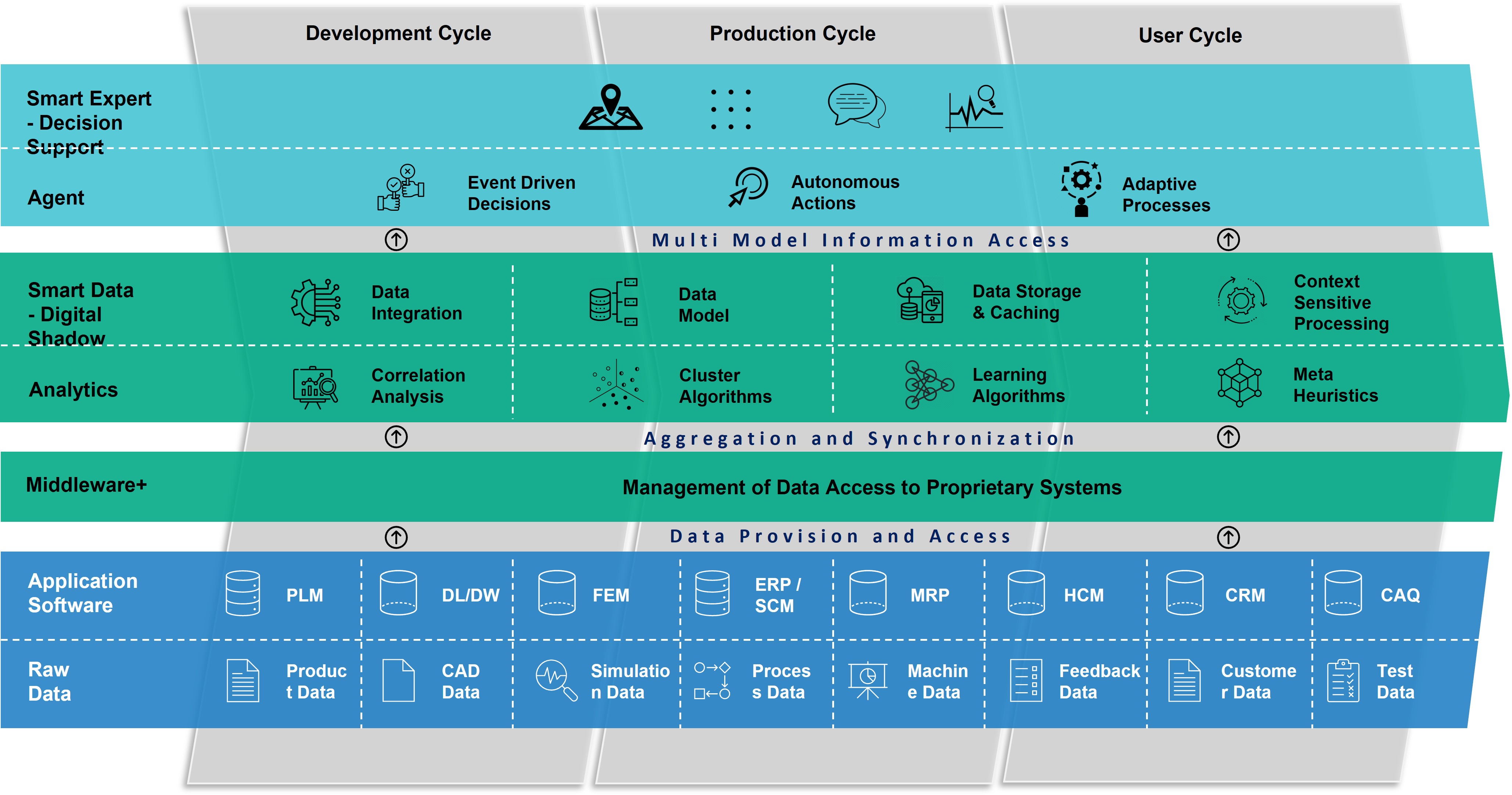
Overview:
Industry 4.0 focuses on the end to end digitization of all physical assets and integration into digital ecosystems with value chain partners. Generating, analyzing and communicating data seamlessly supports the gains promised by Industry 4.0, which networks a wide range of new technologies to create value.
- DIGITIZATION AND INTEGRATION OF VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL VALUE CHAINS: Digitize and integrate processes vertically across the entire organization, from product development and purchasing, through manufacturing, logistics and service All data about operations processes, process efficiency and quality management, as well as operations planning are available real time, supported by augmented reality and optimized in an integrated network
- DIGITIZATION OF PRODUCT AND SERVICE OFFERINGS: Digitization of products includes the expansion of existing products, e g by adding smart sensors or communication devices that can be used with data analytics tools, as well as the creation of new digitized products which focus on completely integrated solutions
- DIGITAL BUSINESS MODELS AND CUSTOMER ACCESS: Expand offering by providing disruptive digital solutions such as complete, data driven services and integrated platform solutions Disruptive digital business models are often focused on generating additional digital revenues and optimizing customer interaction and access
Challenges:
Here are four major challenges faced by many organizations converting these to opportunities makes the transformation journey faster smarter and scalable.
- A GAP IN TECHNICAL SKILLS: The needs required of the workforce all evolving. Only with the right workforce will business models be able to successfully implement new technology and maintain operations.
- DATA GROWTH & SENSITIVITY: The rise in technology has also led to increasing concerns over data and IP privacy, ownership, and management. Current data governance policies for internal use within organizations are inadequate to support cross organizational data sharing.
- INTEROPERABILITY: Another significant issue is the lack of separation between protocols, components, products, and systems. Unfortunately, interoperability impedes companies’ ability to innovate.
- SECURITY: Threats in terms of current and emerging vulnerabilities in the factory are another significant concern. The physical and digital systems that make up smart factories make real-time interoperability possible—however, it comes with the risk of an expanded attack surface.
Solutions:
Industry 4.0 solutions improve operations efficiency, productivity, product quality, inventory management, asset utilization, time to market, agility, workplace safety and environmental sustainability. Here are some of the solutions by business functions.
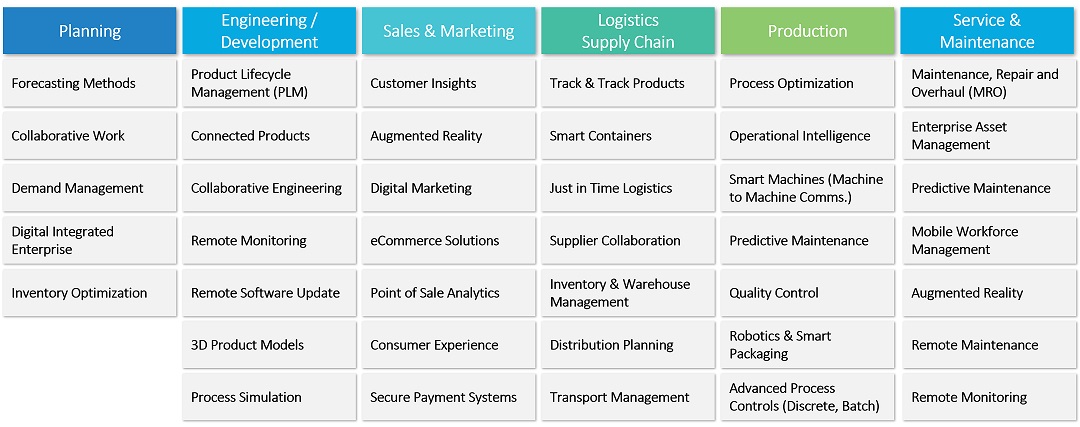
Smart Factory Landscape: